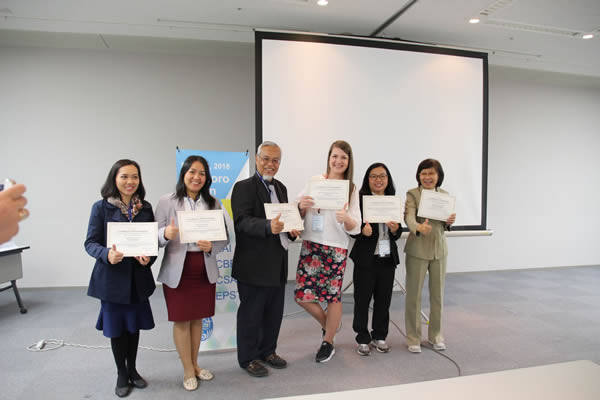
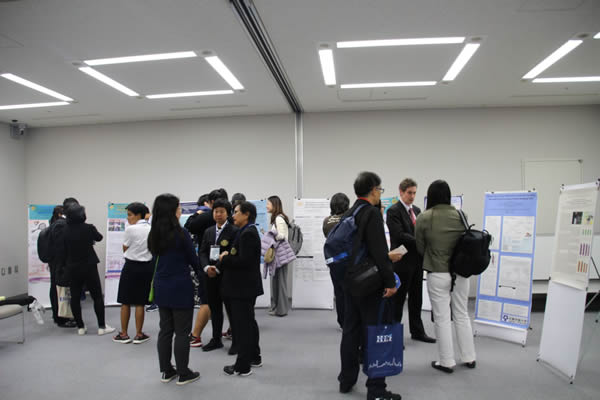
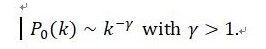2018 ICEAI @ Hokkaido
The 8th International Congress on Engineering and Information
May 1-4 2018 in Hokkaido, Japan
Keynote Speaker
Tae Yoon Kim
Professor
Department of Statistics, Keimyung University
Topic: Complex Network in Big Data Problems
Abstract Systems as diverse as brain or genetic networks are best described as networks with complex topology. A common topological property of many large networks is that the network connectivity generated by a few influential nodes follow a scale-free distribution. The scale-free (power-law) distribution is given by the probability that one vertex in the network interacts withother vertices decays as a power law, following
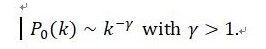
It has been well understood that two important general components, growth and preferential attachment, generate such scale-free distribution. The growth is defined as the increase of the number of nodes of the network over time and the preferential attachment as assigning the probabilityin a way that at a given time a new vertex connects vertexproportional to the already given connectivityof that vertex. In this talk, we discuss scale-free network and the two components in statistical point of view and then propose test statistics which enable to carry out formal statistical test against scale-free network.
We also discuss scale-free distribution in various types of big data problems, which includes social network, computer network, economic crisis, motor learning, language learning, city heavy rain, genetics and brain network.
Delmar R. Arzabal, MSc
Radiation Oncology Medical Physicist
Topic: Medical Imaging in Radiation Oncology and Beyond
Abstract
Modern medical diagnosis and treatment heavily rely on the imaging modality. In the field of medical physics, different imaging modalities, particularly those that utilize electromagnetic waves, are thoroughly studied. X-rays are commonly used and its applications vary extensively based on the complexity of the target volume to give 2D and 3D images. 3-dimensional images are easily rendered using Computed Tomography (CT) scan. The data of which can be integrated with Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) for better tumor localization and cancer prognosis.
Advancements in radiotherapy allow the medical physicists to target and treat the tumor volume more accurately. However, contouring the actual body part still highly depends on the image quality. Various image quality enhancements can be done through the modification virtual and physical parameters of data acquisition. Image reconstruction can be analytic or iterative. Both methods utilize algorithms, commonly the Fourier Transform in 1 and 2 dimensions. Mathematical computation and strategic estimation have considerable effects on the reconstructed image.
The CT information can be further differentiated to isolate a chosen part and to export data for 3D printing.This permits customized treatment accessories which can improve radiation dose delivery to patients. The utilization of the image data to 3D print a treatment accessory or replicate an anatomical part is not only useful for radiation oncology, but extends to biomedical engineering and other allied sciences.
onference Venue
Sapporo Convention Center
ADD: 1-1-1 Higashi-Sapporo 6-jo, Shiroishi-ku, Sapporo, 003-0006, Japan
TEL: +81-11-817-1010